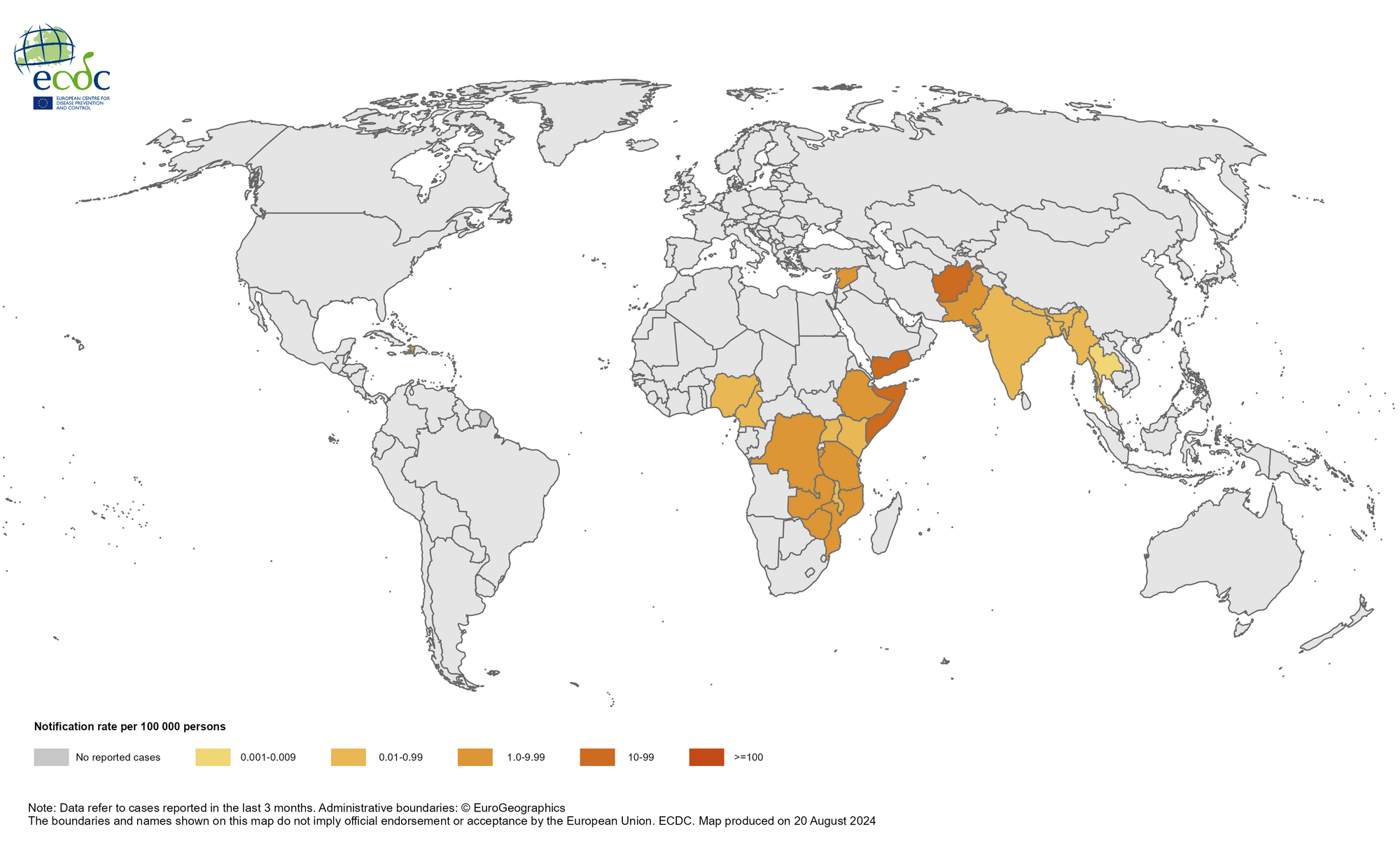
Since 30 June 2024 and as of 31 July 2024, 63 372 new cholera cases, including 187 new deaths, have been reported worldwide.
The five countries reporting most cases are Afghanistan (24 951), Yemen (12 825), Pakistan (12 503), Ethiopia (3 491) and Haiti (2 715).
The five countries reporting most new deaths are Yemen (47), Ethiopia (46), Nigeria (28), Haiti (22) and United Republic of Tanzania (11).
In addition, 46 016 new cases were reported or collected retrospectively from before 1 June 2024.
New cases have been reported from Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Burundi, Cameroon, Comoros, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, Haiti, Kenya, Mozambique, Myanmar, Nepal, Nigeria, Pakistan, Somalia, Thailand, United Republic of Tanzania, Yemen, Zambia, and Zimbabwe.
Since 1 January 2024 and as of 31 July 2024, 312 135 cholera cases, including 2 284 deaths, have been reported worldwide
Countries with most cases Yemen, Ethiopia, Nigeria, Haiti Travel-related cases Few reported each year in the EU/EEA Vaccination for travellers at higher risk is recommended, such as emergency and relief workers
Burundi : Since 30 June 2024 and as of 28 July 2024, 118 new cases have been reported. Since 01 January 2024 and as of 28 July 2024, 646 cases, including 1 death has been reported. In comparison, in 2023 and as of 09 July 2023, 574 cases, including 9 deaths were reported.
Cameroon : Since 30 June 2024 and as of 28 July 2024, 28 new cases have been reported. Since 01 January 2024 and as of 28 July 2024, 439 cases have been reported. In comparison, in 2023 and as of 02 July 2023, 3 787 cases, including 138 deaths were reported.
Comoros : Since 30 June 2024 and as of 28 July 2024, 458 new cases, including 3 new deaths have been reported. Since 01 January 2024 and as of 28 July 2024, 10 329 cases, including 149 deaths have been reported. In comparison, in 2023 and as of 01 August 2023, no cases were reported.
Democratic Republic of the Congo : Since 30 June 2024 and as of 28 July 2024, 1 621 new cases, including 9 new deaths have been reported. Since 01 January 2024 and as of 28 July 2024, 21 764 cases, including 307 deaths have been reported. In comparison, in 2023 and as of 15 July 2023, 23 926 cases, including 178 deaths were reported.
Ethiopia : Since 16 June 2024 and as of 28 July 2024, 3 491 new cases, including 46 new deaths have been reported. Since 01 January 2024 and as of 28 July 2024, 21 287 cases, including 182 deaths have been reported. In comparison, in 2023 and as of 02 July 2023, 11 425 cases, including 142 deaths were reported.
Kenya : Since 16 June 2024 and as of 28 July 2024, 30 new cases, including 2 new deaths have been reported. Since 01 January 2024 and as of 28 July 2024, 295 cases, including 3 deaths have been reported. In comparison, in 2023 and as of 29 June 2023, 8 735 cases, including 137 deaths were reported
Mozambique: Since 30 June 2024 and as of 28 July 2024, 62 new cases have been reported. Since 01 January 2024 and as of 28 July 2024, 8 171 cases, including 17 deaths have been reported. In comparison, in 2023 and as of 16 July 2023, 32 983 cases, including 137 deaths were reported.
Nigeria: Since 30 June 2024 and as of 19 July 2024, 1 230 new cases, including 28 new deaths have been reported. Since 01 January 2024 and as of 19 July 2024, 2 809 cases, including 82 deaths have been reported. In comparison, in 2023 and as of 30 July 2023, 2 309 cases, including 57 deaths were reported.
Somalia: Since 30 June 2024 and as of 28 July 2024, 1 660 new cases, including 7 new deaths have been reported. Since 01 January 2024 and as of 28 July 2024, 16 569 cases, including 134 deaths have been reported. In comparison, in 2023 and as of 02 July 2023, 10 686 cases, including 30 deaths were reported.
United Republic of Tanzania: Since 30 June 2024 and as of 28 July 2024, 418 new cases, including 11 new deaths have been reported. Since 01 January 2024 and as of 28 July 2024, 3 719 cases, including 63 deaths have been reported. In comparison, in 2023 and as of 30 July 2023, 87 cases, including 3 deaths were reported.
Zambia: Since 22 June 2024 and as of 19 July 2024, 4 new cases have been reported. Since 01 January 2024 and as of 19 July 2024, 20 063 cases, including 612 deaths have been reported. In comparison, in 2023 and as of 22 June 2023, 757 cases, including 14 deaths were reported.
Zimbabwe: Since 30 June 2024 and as of 06 July 2024, 3 new cases, including 1 new death has been reported. Since 01 January 2024 and as of 06 July 2024, 19 412 cases, including 386 deaths have been reported. In comparison, in 2023 and as of 09 July 2023, 3 430 cases, including 78 deaths were reported.
Dominican Republic : Since 15 December 2023 and as of 26 April 2024, 113 new cases, including 1 new death has been reported. Since 01 January 2024 and as of 26 April 2024, 113 cases, including 1 death has been reported. In comparison, in 2023 and as of 15 June 2023, 99 cases were reported.
Haiti : Since 18 May 2024 and as of 27 July 2024, 2 715 new cases, including 22 new deaths have been reported. Since 01 January 2024 and as of 27 July 2024, 9 478 cases, including 141 deaths have been reported. In comparison, in 2023 and as of 10 July 2023, 33 058 cases, including 405 deaths were reported.
Afghanistan : Since 29 June 2024 and as of 27 July 2024, 24 951 new cases, including 10 new deaths have been reported. Since 01 January 2024 and as of 27 July 2024, 95 301 cases, including 48 deaths have been reported. In comparison, in 2023 and as of 09 July 2023, 91 052 cases, including 43 deaths were reported.
Bangladesh : Since 08 July 2024 and as of 29 July 2024, 29 new cases have been reported. Since 01 January 2024 and as of 29 July 2024, 99 cases have been reported. In comparison, in 2023 and as of 24 May 2023, 34 609 cases were reported.
Myanmar : As of 15 July 2024, 1 141 new cases, including 1 new death has been reported. Since 01 January 2024 and as of 15 July 2024, 1 141 cases, including 1 death has been reported. In comparison, in 2023 and as of 01 August 2023, no cases were reported.
Nepal : Since 05 September 2022 and as of 28 July 2024, 20 new cases have been reported. Since 01 January 2024 and as of 28 July 2024, 20 cases have been reported. In comparison, in 2023 and as of 01 August 2023, no cases were reported.
Pakistan : Since 10 June 2024 and as of 15 July 2024, 12 503 new cases have been reported. Since 01 January 2024 and as of 15 July 2024, 38 636 cases have been reported. In comparison, in 2023 and as of 15 July 2023, 10 998 cases were reported.
Thailand: Since 27 June 2024 and as of 31 July 2024, 4 new cases have been reported. Since 01 January 2024 and as of 31 July 2024, 9 cases have been reported. In comparison, in 2023 and as of 26 March 2023, 1 case were reported.
Yemen : Since 17 June 2024 and as of 22 July 2024, 12 825 new cases, including 47 new deaths have been reported. Since 01 January 2024 and as of 22 July 2024, 24 308 cases, including 140 deaths have been reported. In comparison, in 2023 and as of 11 June 2023, 3 878 cases, including 4 deaths were reported.
In 2022, 29 cases were reported by nine EU/EEA countries , while two were reported in 2021 and none in 2020. In 2019, 25 cases were reported in EU/EEA countries. All cases had a travel history to cholera-affected areas.
Cholera cases have continued to be reported in Africa and Asia in recent months. Cholera outbreaks have also been reported in parts of the Middle East and the Americas.
In this context, although the risk of cholera infection for travellers visiting these countries remains low, sporadic importation of cases to the EU/EEA is possible.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), vaccination should be considered for travellers at higher risk, such as emergency and relief workers who are likely to be directly exposed.
Vaccination is generally not recommended for other travellers. Travellers to cholera-endemic areas should seek advice from travel health clinics to assess their personal risk and apply precautionary sanitary and hygiene measures to prevent infection. Such measures can include drinking bottled water or water treated with chlorine, carefully washing fruit and vegetables with bottled or chlorinated water before consumption, regularly washing hands with soap, eating thoroughly cooked food, and avoiding the consumption of raw seafood products.
ECDC continues to monitor cholera outbreaks globally through its epidemic intelligence activities in order to identify significant changes in epidemiology and provide timely updates to public health authorities. Reports are published on a monthly basis.
Disclaimer: Data presented in this report originate from several sources, both official public health authorities and non-official, such as the media. Data completeness depends on the availability of reports from surveillance systems and their accuracy, which varies between countries. All data should be interpreted with caution as there may be areas of under-reporting and figures may not reflect the actual epidemiological situation.